Google Chrome Zero-Day CVE-2025-2783 Exploited in APT Group TaxOff Campaigns
Summary
A newly-patched zero-day vulnerability in Google Chrome CVE-2025-2783 which was exploited in the wild by a threat actor TaxOff, leading to the deployment of Trinper which an advanced backdoor.
The CVE-2025-2783 exploited a sandbox escape vulnerability within Google Chrome’s Mojo IPC (Inter-Process Communication) framework, which allowed attackers to bypass the browser’s security sandbox and lead to RCE.
TaxOff Threat Actor
TaxOff is a highly sophisticated Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) group primarily targeting government organizations which is known for its use of advanced social engineering tactics, often involving phishing campaigns that exploit themed around financial reporting and regulatory compliance.
The CVE-2025-2783 vulnerability was first detected in March 2025 after Kaspersky reported real-world exploitation.
TaxOff used a phishing-based delivery method, which involved embedding a malicious link in emails masquerading as invitations to legitimate events like the Primakov Readings forum.
Once the link was clicked, the CVE-2025-2783 exploit was triggered, leading to the deployment of the Trinper backdoor. It was a one-click compromise that delivered a highly tailored payload with surgical precision.
Trinper Backdoor
This is a multi-threaded C++ backdoor that collected host data, logged keystrokes, exfiltrated targeted documents like document, excel or pdf files and maintained remote access.
But this wasn’t just a “plug-and-play” backdoor. Trinper’s loader employed five layers of encryption, utilizing ChaCha20, modified BLAKE2b hashes, and even machine-specific environmental checks. It was decrypted only on intended systems, using unique hardware identifiers like firmware UUIDs and PEB structures.
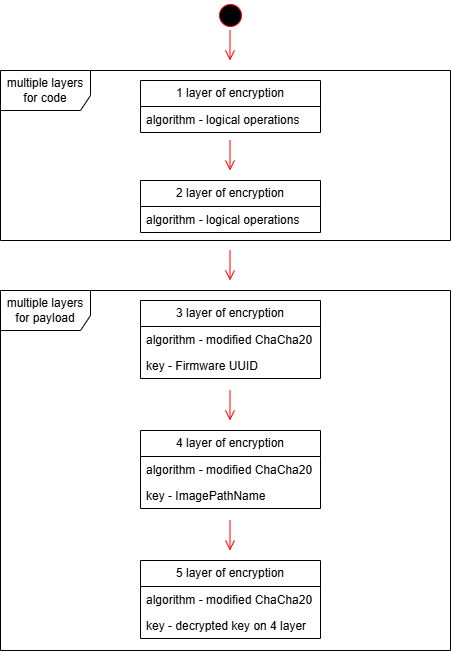
Source: global.ptsecurity.com
Interestingly, researchers found that Team46, a different APT group shares many similarities with TaxOff in terms of TTPs. This overlap raises the possibility that TaxOff and Team46 are the same group operating under different aliases.
Both groups have used PowerShell-based loaders and Cobalt Strike as their primary exploitation vectors.
This flaw allows threat actors to:
- Execute arbitrary code
- Bypass Chrome’s built-in security sandbox
- Potentially gain remote control over the system
Recommendation
The rapid exploitation of CVE-2025-2783 highlights the critical importance of timely patch management. Google released a fix for this vulnerability in March 2025, and all users are strongly advised to update their Chrome browsers to the latest version immediately.
In addition to patching, organizations should implement the following defensive measures
- Enhance email filtering systems and provide regular phishing awareness training for employees.
- Continuously monitor systems for unusual or suspicious behavior related to script execution or network anomalies.
- Restrict the execution of unsigned or obfuscated scripts and macros, particularly in email attachments or downloaded files, using tools like AppLocker or Microsoft Defender ASR.
References:
