Decade-Old Threat: CVE-2018-8639 Still Poses Risks to Unpatched Windows Systems
CVE-2018-8639 is a privilege escalation flaw in the Win32k component of Microsoft Windows that lets attackers run any code in kernel mode. This vulnerability, which was first fixed by Microsoft in December 2018, still poses a risk to unpatched computers.
| OEM | Microsoft |
| Severity | High |
| CVSS | 7.8 |
| CVEs | CVE-2018-8639 |
| Exploited in Wild | Yes |
| Patch/Remediation Available | Yes |
| Advisory Version | 1.0 |
Overview on Vulnerability
The vulnerability gives hackers the ability to install persistent malware, get around security measures, and alter system operations covertly. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has included this vulnerability in its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, further highlighting its ongoing threat.
| Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Severity |
| Privilege Escalation Vulnerability | CVE-2018-8639 | Windows | High |
Technical Summary
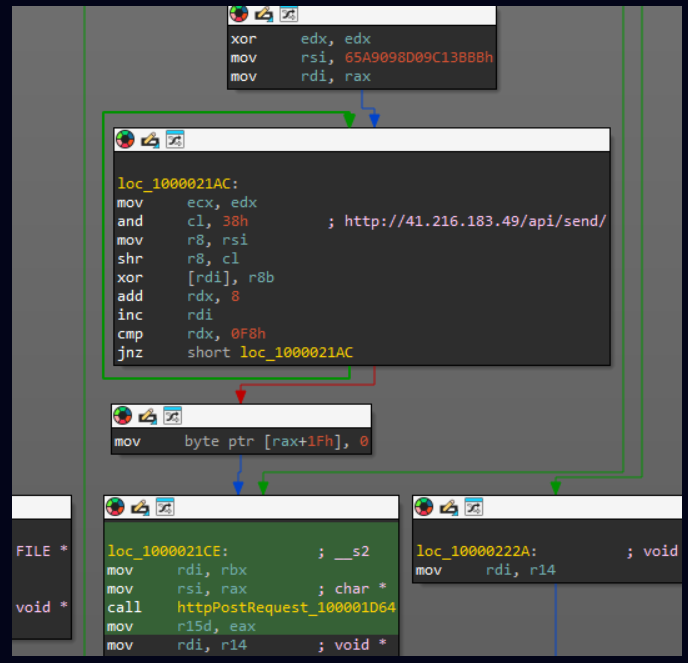
The vulnerability exists within the Win32k.sys driver, which handles graphical user interface (GUI) interactions.
Designated as CWE-404: Improper Resource Shutdown or Release, the flaw enables authenticated local attackers to improperly release system resources, leading to privilege escalation. Exploiting this vulnerability grants kernel-mode execution rights, allowing attackers to bypass security mechanisms, install persistent malware, and manipulate system functions without detection.
| CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
| CVE-2018-8639 | Windows 7, 8.1, 10, RT 8.1, Windows Server 2008, 2008 R2, 2012, 2012 R2, 2016, 2019 | Improper Resource Shutdown or Release in Win32k.sys driver, enabling privilege escalation. | System compromise, unauthorized access, potential malware persistence |
Remediation:
- Organizations and individuals must apply Microsoft’s security updates released in December 2018 (KB4483235) to mitigate the risk.
- Additionally, it is essential to apply all available updates from Windows to ensure comprehensive protection against known vulnerabilities.
General Recommendations:
- Implement network segmentation to isolate critical assets and minimize the impact of potential security breaches.
- Adopting the principle of least privilege (PoLP) to limit user access.
- Continuous monitoring of anomalous kernel-mode activities.
Conclusion:
Unpatched Windows systems are particularly vulnerable, especially in industrial control systems (ICS) and healthcare facilities where obsolete software is ubiquitous. While Microsoft has fixed the issue, firms that rely on legacy systems must implement additional security measures. Cyber adversaries are always refining their exploitation techniques, making proactive security strategies critical to reducing risk.
References:
- https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/cve-2018-8639
- https://github.com/ze0r/CVE-2018-8639-exp