16 Billion Passwords Leaked in Largest Data Breach; Impact of Infostealer Malware
Data Breach with 30 exposed Datasets & contained approx 10 to 3.5 billion records making it one of the largest data breach.
According to a report security researchers from Cybernews found about a Data breach that leaked important data or passwords that was mostly generated by various cybercriminals using info stealing malware. They exposed data was made to look like a breach but these login credentials were gathered from social media, corporate platforms, VPNs etc via infostealer.
Now cybercriminals have unprecedented access to personal credentials and these credentials be used for account takeover, identity theft and targeted phishing activities.
The concern is the structure and recency of these datasets as they are not old breaches being recycled. This is fresh, weaponizable intelligence at scale”, added researchers.
The data sets contains a mix of details from stealer malware, credential stuffing sets and repackaged leaks. There is no way to compare these datasets, but likely to contain at least some duplicated information. This makes it hard to determine how many people were affected by the data breach.
What are Data sets & how deadly can be Infostealer as a malware?
Datasets are basically structure collection of data collected over the years or so and organized as case specific models
In 2024 datasets containing billions of passwords have previously found their way on the internet. Last year, researchers came across what they called the Mother of All Breaches, which contained more than 26 billion records.
The data breach that happened had data in sets, following a particular pattern, containing an URL followed by a username and password. To those unaware, this is exactly how infostealing malware collects information and sends it to threat actors.
The exposed data came from platforms widely used round the world starting from Google, Apple, Github, Telegram & Facebook. So data was first collected over a period of time, further made into data sets and grouped together.
Info stealers are malware programs that are designed to silently steal usernames and passwords Basically designed to swipe of credentials from people’s devices and send them to threat actors for further them for sale on dark web forums.
An infostealer is malware that attempts to steal credentials, cryptocurrency wallets, and other data from an infected device. Over the years, infostealers have become a massive problem, leading to breaches worldwide. No device is spare from infostealer’s impact including Windows and Macs, and when executed, will gather all the credentials it can find stored on a device and save them in what is called a “log.”
If a organization or individual is infected with an infostealer and have hundreds of credentials saved in their browser, the infostealer will steal them all and store them in the log. These logs are then uploaded to the threat actor, where the credentials can be used for further attacks or sold on cybercrime marketplaces.
An infostealer log is generally an archive containing numerous text files and other stolen data.
Fig1:
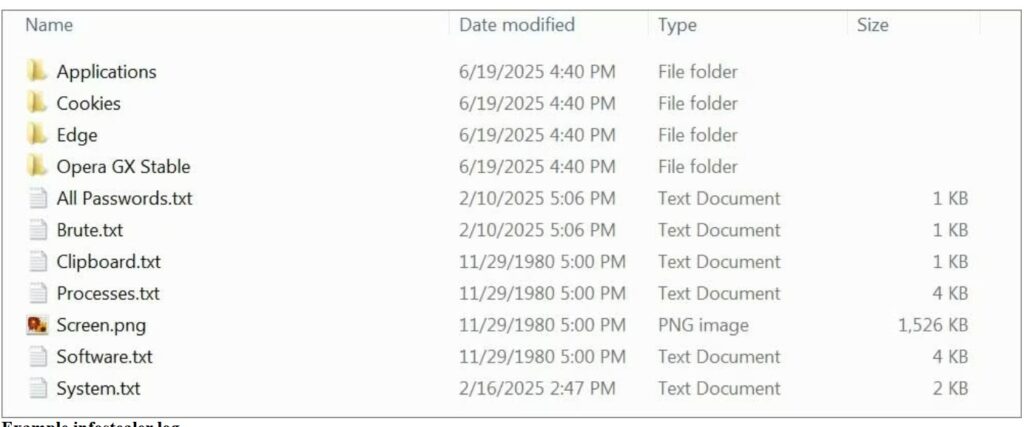
(Image courtesy: Bleeping computers)
A devastating data breach is a nightmare for customers and affected organizations, but breaches can have a positive side also. Each incident is a learning opportunity. It’s easier to defend critical data when we understand the mistakes made by others and the tactics used by attackers.
How to be secure & keep your Data safe
If users are in midst of data breach or may find that their data is not safe as an infostealer might be there in your systems or devices then scan your device with an antivirus program. Once done then change password or your newly entered credentials could be stolen again. The system is clean so password hygiene can be maintained time to time.
At times even unique passwords won’t help you stay protected if you are hacked, fall for a phishing attack, or install malware. Its better not to change all credentials in one go instead having a cyber security hygiene in routine is better as an option.
Intru360
For organizations to stop and detect any intrusion by attackers prefer to have Intru360 in your list of cyber security go to products from Intruceptlabs.
Intru360 gives security analysts and SOC managers a clear view across the organization, helping them fully understand the extent and context of an attack. It also simplifies workflows by automatically handling alerts, allowing for faster detection of both known and unknown threats.
Globally every year cyberattacks are growing and mutating each month. Organizations have their Intelligent intrusion network detection systems in place analyze and detect anomalous traffic to face these threats.
Do visit our website for more information.




