OEM | Microsoft |
Severity | High |
Date of Announcement | 2024-11-13 |
NO. of Vulnerabilities Patched | 89 |
Actively Exploited | 02 |
Exploited in Wild | Yes |
Advisory Version | 1.0 |
Microsoft’s November 2024 Patch Tuesday release addresses 89 security vulnerabilities across various products, including critical updates for Windows, Microsoft Edge, SQL Server, and more. Four zero-day vulnerabilities are part of this release, with two actively exploited in the wild. The patch targets a range of critical issues across Microsoft products, categorized as follows:
Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Impact | CVSS Score |
Microsoft Management Console Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (Exploitation detected) | CVE-2024-43572 | Windows Servers and Windows 10&11 | High | 7.8 |
Winlogon Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | CVE-2024-43583 | Windows systems using Winlogon | High | 7.8 |
Windows Hyper-V Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | CVE-2024-20659 | Windows Hyper-V | High | 7.1 |
Windows MSHTML Platform Spoofing Vulnerability | CVE-2024-43573 | Windows Servers and Windows 10&11 | Medium | 6.5 |
CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
CVE-2024-49039 | Windows Servers and Windows 10&11 | This zero-day allows attackers to escalate privileges within Windows environments. Exploited actively, it is particularly concerning for its ability to grant attackers elevated access. | Elevation of privilege potentially leading to full system control. |
CVE-2024-49019 | Windows Servers | A flaw in Active Directory Certificate Services allows attackers to gain domain administrator privileges by exploiting misconfigured version 1 certificate templates with overly broad enrollment permissions. This can be triggered by an attacker crafting a certificate request that bypasses security controls. | Elevate privileges to domain administrator, compromising the entire Active Directory environment and enabling full network control. |
CVE-2024-49040 | Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 and 2019 | A vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange Server allows attackers to spoof the sender’s email address in emails to local recipients by exploiting improper verification of the P2 FROM header. This flaw can be used to launch email-based phishing and social engineering attacks. | Attackers can impersonate trusted senders, deceiving recipients into trusting malicious emails, potentially leading to data compromise or malware infections. |
CVE-2024-43451 | Windows Servers and Windows 10&11 | A zero-day that exposes NTLMv2 hashes, enabling “pass-the-hash” attacks for unauthorized network access. This is the third NTLM-related zero-day discovered in 2024. | High risk in network environments; attackers may impersonate users and compromise critical systems. |
OEM | Palo Alto |
Severity | Critical |
Date of Announcement | 2024-07-10 |
CVSS Score | 9.3 |
CVE | CVE-2024-5910 |
CWE | CWE-306 |
Exploited in Wild | Yes |
Patch/Remediation Available | Yes |
Advisory Version | 1.0 |
CISA has included the Palo Alto Networks Expedition tool Missing Authentication Vulnerability in its catalog of actively exploited vulnerabilities. Palo Alto’s Expedition is a migration tool designed to simplify the process of transferring configurations from other vendors to Palo Alto Networks. The issue is tracked under CVE-2024-5910. The vulnerability, which involves missing authentication for a critical function in Expedition, could allow attackers with network access to take over an admin account. This poses a risk to imported configuration secrets, credentials, and other sensitive data within Expedition.
Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Severity | Fixed Version |
Palo Alto Networks Expedition Missing Authentication Vulnerability | CVE-2024-5910 | Expedition | Critical | Expedition 1.2.92 and all later versions |
CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
CVE-2024-5910 | Expedition from 1.2 before 1.2.92 | The vulnerability, caused by missing authentication for an important function in Expedition, could allow attackers with network access to take over an admin account. | Account Takeover |
OEM | VMware |
Severity | Critical |
Date of Announcement | 2024-10-23 |
CVSS Score | 9.8 |
CVE | CVE-2024-38812, CVE-2024-38813 |
Exploited in Wild | Yes |
Patch/Remediation Available | Yes |
Advisory Version | 1.0 |
Critical vulnerabilities have been identified in the vCenter Server that require immediate action. A heap overflow vulnerability in the DCE/RPC protocol could allow a malicious actor with network access to execute remote code by sending specially crafted packets. Additionally, there is a privilege escalation vulnerability that enables an attacker to escalate privileges to root using a similar method. Both vulnerabilities pose significant risks, and it is essential to implement remediation measures promptly to protect your vCenter Server and associated assets.
Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Severity | Fixed Version |
VMware vCenter Server heap-overflow vulnerability | CVE-2024-38812 | VMware vCenter Servers and VMware Cloud Foundation | Critical | 7.0 U3t, 8.0 U3d and U2e (vCenter Server) Async Patch for VMware Cloud Foundation |
VMware vCenter privilege escalation vulnerability | CVE-2024-38813 | VMware vCenter Servers and VMware Cloud Foundation | Critical | 7.0 U3t, 8.0 U3d and U2e (vCenter Server) |
CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
CVE-2024-38812 | VMware vCenter Server 7.0 and 8.0, VMware Cloud Foundation 4.x and 5.x | The critical vulnerability is caused by a heap overflow in vCenter Server's DCE/RPC protocol implementation. This allows an unauthenticated attacker to remotely execute arbitrary code without user interaction. | Remote code execution. |
CVE-2024-38813 | VMware vCenter Server 7.0 and 8.0, VMware Cloud Foundation 4.x and 5.x | This is a privilege escalation vulnerability in VMware vCenter Server that allows attackers with network access to escalate their privileges to root by exploiting an improper permission management flaw. By sending specially crafted network packets, a malicious actor can completely takeover the target. | Full administrative control. |
Administrators are strongly advised to update their VMware vCenter Server to the latest available versions:
Restrict network access to vCenter Server by configuring firewalls to allow access only from trusted IP addresses.
Monitor for Indicators of Compromise (IoCs):Security teams should monitor logs and network traffic for unusual activity, including unexpected traffic to or from the vCenter Server.
A rapidly escalating cyber threat targeting WordPress sites with malicious plugins. Malicious actors are breaching WordPress websites to install rogue plugins, which display fake software updates and error messages. These are being used to distribute information-stealing malware.
Since 2023, a malicious campaign known as ClearFake has been exploiting compromised websites to display fake browser update banners that trick users into downloading malware. This campaign evolved in 2024 with the introduction of ClickFix, a more advanced variant. ClickFix campaigns are more sophisticated and use fake error messages for browsers, web conferences, social media platforms, and even captcha pages to mislead users. The supposed “fixes” are actually PowerShell scripts designed to install malware capable of stealing sensitive information, such as login credentials.
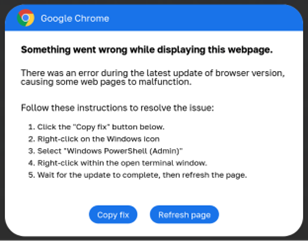
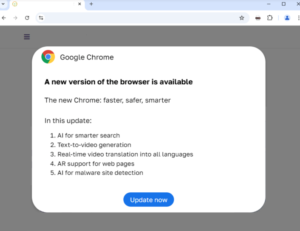
An example ClickFix overlay pretending to be a Chrome error Fake Google update banner
Source: BleepingComputer Source: Randy McEoin
Bleepingcomputer reported that over 6,000 WordPress sites have been compromised as part of this campaign. The attackers are installing malicious plugins that closely resemble legitimate ones, such as “Wordfence Security” or “LiteSpeed Cache,” to evade detection. These plugins secretly inject malicious JavaScript into the HTML of affected websites, leading to the display of fraudulent updates or error messages.
Here is the list of malicious plugins identified from June to September 2024:
LiteSpeed Cache Classic | Custom CSS Injector |
MonsterInsights Classic | Custom Footer Generator |
Wordfence Security Classic | Custom Login Styler |
Search Rank Enhancer | Dynamic Sidebar Manager |
SEO Booster Pro | Easy Themes Manager |
Google SEO Enhancer | Form Builder Pro |
Rank Booster Pro | Quick Cache Cleaner |
Admin Bar Customizer | Responsive Menu Builder |
Advanced User Manager | SEO Optimizer Pro |
Advanced Widget Manage | Simple Post Enhancer |
Content Blocker | Social Media Integrator |
The threat actors appear to be utilizing stolen admin credentials to directly log into WordPress sites. These credentials are likely obtained through a combination of brute force attacks, phishing, or pre-existing malware infections. Once they gain access, the attackers are able to install these plugins without the need to visit the login page, streamlining the attack process.
If you are using a WordPress site, we recommend the following immediate actions:
OEM | Veeam |
Severity | Critical |
Date of Announcement | 2024-10-17 |
CVSS Score | 9.8 |
CVE | CVE-2024-40711 |
CWE | CWE-502 |
Exploited in Wild | Yes |
Patch/Remediation Available | Yes |
Advisory Version | 1.0 |
Veeam Backup & Replication software has been found to contain a critical vulnerability (CVE-2024-40711) that is actively being exploited by ransomware actors to distribute Akira and Fog ransomware. This vulnerability allows remote code execution without authentication, which can result in complete system compromise. Attackers are using this security gap to establish unauthorized accounts with administrative rights and spread ransomware on systems that lack protection.
Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Impact | CVSS Score |
Veeam Backup & Replication Critical Code Execution Vulnerability | CVE-2024-40711 | Veeam Backup & Replication | Critical | 9.8 |
CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
CVE-2024-40711 | Veeam Backup & Replication versions prior to 12.2.0.334 | CVE-2024-40711 is a deserialization of untrusted data flaw that can be exploited via a URI /trigger on port 8000. Once exploited, the vulnerability triggers Veeam.Backup.MountService.exe to create a local account named "point" with administrative and Remote Desktop User privileges. Attackers then use this access to deploy ransomware such as Akira and Fog, and in some cases, exfiltrate data using tools like Rclone. | Remote code execution, creation of unauthorized admin accounts, ransomware deployment (Akira and Fog), data exfiltration. |
OEM | Fortinet |
Severity | Critical |
Date of Announcement | 2024-10-16 |
CVSS Score | 9.8 |
CVE | CVE-2024-23113 |
CWE | CWE-134 |
Exploited in Wild | Yes |
Patch/Remediation Available | Yes |
Advisory Version | 1.0 |
A Critical vulnerability (CVE-2024-23113) has been identified in the FortiOS fgfmd daemon, which enables unauthenticated attackers to remotely execute arbitrary code or commands. This flaw arises from a format string vulnerability (CWE-134) within the fgfmd daemon, where specially crafted requests can initiate arbitrary code execution, potentially resulting in full system compromise. Affected versions include multiple releases of FortiOS, FortiPAM, FortiProxy, and FortiWeb.
Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Impact | CVSS Score |
Fortinet Products Format Sting Vulnerability | CVE-2024-23113 | FortiOS, FortiProxy, FortiPAM, FortiWeb | Critical | 9.8 |
CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
CVE-2024-23113 | FortiOS (7.4.0-7.4.2, 7.2.0-7.2.6, 7.0.0-7.0.13), FortiProxy (7.4.0-7.4.2, 7.2.0-7.2.8, 7.0.0-7.0.15), FortiPAM (1.2 and lower), FortiWeb (7.4.0-7.4.2) | The vulnerability lies in the fgfmd daemon’s handling of format strings in incoming requests, which can be exploited by remote attackers via crafted inputs. Exploitation of this flaw allows attackers to execute unauthorized code or commands on the affected systems. | Remote Code Execution (RCE) |
Fortinet has released security patches addressing this vulnerability. Here is the below patched versions for the Fortinet products.
OEM | Microsoft |
Severity | Critical |
Date of Announcement | 2024-10-10 |
NO. of Vulnerabilities Patched | 117 |
Exploitable Vulnerabilities | 02 |
Exploited in Wild | Yes |
Advisory Version | 1.0 |
Microsoft’s October 2024 Patch on Tuesday addresses a total of 117 vulnerabilities, including five critical zero-days. This update resolves two actively exploited vulnerabilities and a significant remote code execution issue, while also reintroducing previously mitigated vulnerabilities. The patch targets a range of critical issues across Microsoft products, categorized as follows:
Highlighted below vulnerabilities were publicly known at release, with two actively exploited as zero-days.
Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Impact | CVSS Score |
Microsoft Management Console Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (Exploitation detected) | CVE-2024-43572 | Windows Servers and Windows 10&11 | High | 7.8 |
Winlogon Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | CVE-2024-43583 | Windows systems using Winlogon | High | 7.8 |
Windows Hyper-V Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | CVE-2024-20659 | Windows Hyper-V | High | 7.1 |
Windows MSHTML Platform Spoofing Vulnerability | CVE-2024-43573 | Windows Servers and Windows 10&11 | Medium | 6.5 |
CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
CVE-2024-43572 | Windows Servers and Windows 10&11 | This vulnerability enables attackers to remotely execute code on affected systems, allowing them to take control of the system. | Allows attackers to execute arbitrary code remotely. |
CVE-2024-43583 | Windows systems using Winlogon | Specifically, by abusing a third-party Input Method Editor (IME) during user sign-on. Attackers can exploit this vulnerability to escalate privileges and gain SYSTEM-level access on the affected machine | Allows attackers to gain SYSTEM-level privileges via third-party Input Method Editors (IME) during the Windows sign-in process. |
CVE-2024-20659 | Windows Hyper-V | A vulnerability in Windows Hyper-V that could allow a malicious guest to execute code on the host operating system. It leads to guest-to-host escapes or privilege escalation, making it possible for an attacker to gain elevated access or control of the host machine | Allows guest-to-host escape or privilege escalation |
CVE-2024-43573 | Windows Servers and Windows 10&11 | Improper input handling in web page generation [CWE-79], cross-site scripting)- Exploited by using fake web content that disguises legitimate web pages | Could lead to phishing attacks or data theft. |
OEM | Zimbra |
Severity | Critical |
Date of Announcement | 2024-10-02 |
CVSS Score | 10.0 |
CVE | CVE-2024-45519 |
CWE | -- |
Exploited in Wild | Yes |
Patch/Remediation Available | Yes |
Advisory Version | 1.0 |
A critical vulnerability (CVE-2024-29847) has been identified in Ivanti Endpoint Manager, allowing unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code remotely. This flaw is due to a deserialization of untrusted data issue in the AgentPortal.exe service, specifically within the .NET Remote framework. Exploitation can allow attackers to perform file operations such as reading or writing files on the server, potentially leading to full system compromise.
Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Impact | CVSS Score |
Zimbra - Remote Command Execution | CVE-2024-45519 | Zimbra Collaboration Suite (ZCS) | Critical | 10.0 |
CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
CVE-2024-45519 | Zimbra Collaboration Suite (ZCS) prior to 8.8.15 Patch 46, 9.0.0 Patch 41, 10.0.9, and 10.1.1 | Attackers sent spoofed emails, appearing to be from Gmail, with base64-encoded malicious code in the CC field. This code tricks Zimbra server into executing it as shell commands instead of processing it as email addresses. The goal is to create a web shell on vulnerable servers, enabling remote access and control. Once installed, the web shell listens for specific cookie values to execute commands or download malicious files. | Complete remote control of the affected Zimbra instance. |
In September 2024, Kaspersky reported a widespread attack involving the Necro Trojan, which has potentially infected around 11 million Android devices globally. This sophisticated malware primarily targets users downloading modified versions of popular applications such as Spotify, WhatsApp, and Minecraft, as well as certain apps available on Google Play.
The Necro Trojan is a type of malware that acts as a loader, meaning it can download and execute additional malicious components once it infiltrates a device. Initially discovered in 2019, the Trojan has evolved, integrating advanced features that enhance its evasion techniques and capabilities. The Trojan cleverly hides its malicious payload within seemingly innocuous images, making it difficult to detect using traditional security methods. This technique allows the malware to bypass standard security checks.
Once activated, the Necro loader can:
The Necro Trojan has been found embedded in various applications, both from unofficial sources and Google Play.
To effectively guard against the Necro Trojan and similar threats, users are advised to take the following actions