Critical Security Flaw in Kibana Requires Immediate Attention
Kibana is a robust tool for data visualization and exploration that can be used to search, examine, and track data that is stored in Elasticsearch. A vital part of many organizations’ data analysis procedures, it offers real-time insights through interactive dashboards.
Elastic released security updates to address a critical vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-25012 (CVSS score of 9.9), impacting the Kibana data visualization dashboard software for Elasticsearch.
| OEM | Elastic |
| Severity | Critical |
| CVSS | 9.9 |
| CVEs | CVE-2025-25012 |
| Exploited in Wild | No |
| Patch/Remediation Available | Yes |
| Advisory Version | 1.0 |
Overview
A critical security vulnerability (CVE-2025-25012) has been identified in Kibana, affecting versions 8.15.0 to 8.17.2. The flaw allows attackers to execute arbitrary code, potentially compromising affected systems. Elastic has released a patch in Kibana version 8.17.3to address this issue, and users are strongly advised to update immediately.
| Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Severity |
| Arbitrary code execution Vulnerability | CVE-2025-25012 | Elastic | Critical |
Technical Summary
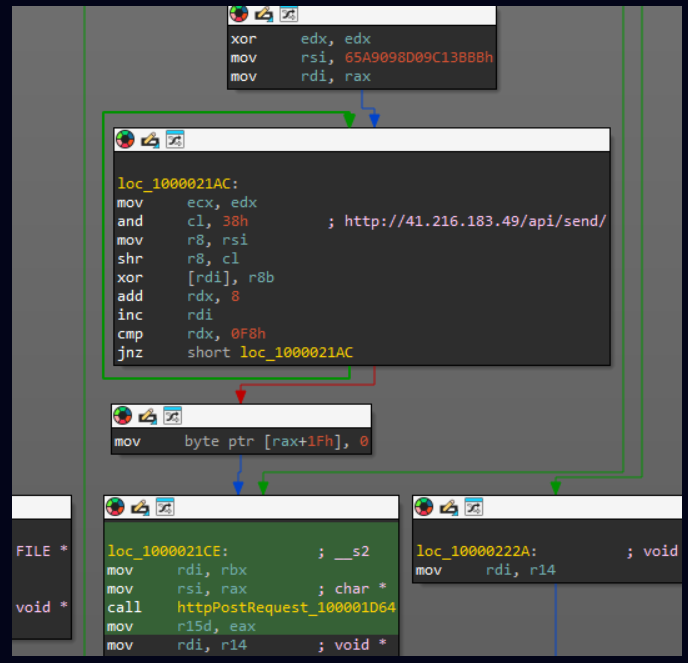
This vulnerability arises from improper handling of JavaScript object prototypes in Kibana’s file upload and HTTP request processing functionalities.
Attackers can exploit this flaw to inject malicious payloads, modify application behavior, and execute arbitrary code. The vulnerability is classified under CWE-1321 (Improper Control of Prototype-Based Attribute Modifications) and aligns with the MITRE ATT&CK framework under tactic T1059 (Command and Scripting Interpreter).
Affected Versions and Exploitation Conditions:
- Kibana 8.15.0 – 8.17.0: Exploitable by users with the Viewer role.
- Kibana 8.17.1 – 8.17.2: Requires privileges fleet-all, integrations-all, and actions:execute-advanced-connectors.
| CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
| CVE-2025-25012 | Kibana 8.15.0 – 8.17.2 | Prototype pollution via crafted file uploads and HTTP requests, allowing manipulation of JavaScript object properties and security controls. | Remote Code Execution, Unauthorized Data Access, Lateral Movement |
Remediation:
- Upgrade: Elastic has released a security patch to address the issue. It is highly recommended to upgrade to Kibana 8.17.3 or a later version
- Temporary Mitigation: If upgrading is not feasible in the short term, apply the following measure to reduce risk:
- Disable the Integration Assistant feature by setting xpack.integration_assistant.enabled: false in kibana.yml.
Conclusion:
Organizations utilizing Kibana should take urgent action to patch CVE-2025-25012 by upgrading to version 8.17.3.
The vulnerability is highly severe, particularly for environments using Kibana for security monitoring, as attackers could exploit this flaw to disable alerts and manipulate detection pipelines. If patching is not immediately possible, temporary mitigations should be applied to reduce the risk of exploitation. Ensuring real-time vulnerability monitoring and implementing strict access controls are also recommended to safeguard against similar threats in the future.
References:
Image